Image
Image

Eyebrow
Blog
Which conventional radiation units are commonly being used?
In this article:
- Conventional radiation units such as the roentgen (R), rad (rd), and curie (Ci) were widely used until 1978 for measuring exposure, absorbed dose, and radioactivity.
- The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) transitioned to SI units in 1978, introducing the gray (Gy), sievert (Sv), and becquerel (Bq) for improved standardization.
- 1 gray (Gy) equals 100 rad, and 1 sievert (Sv) equals 100 rem, aligning absorbed and equivalent dose measurements with international scientific standards.
- 1 curie (Ci) equals 37 gigabecquerels (GBq), providing a modern metric for quantifying radioactivity in industrial and medical applications.
- Understanding both conventional and SI units is essential in industrial radiography for accurate radiation measurement, safety compliance, and global interoperability.
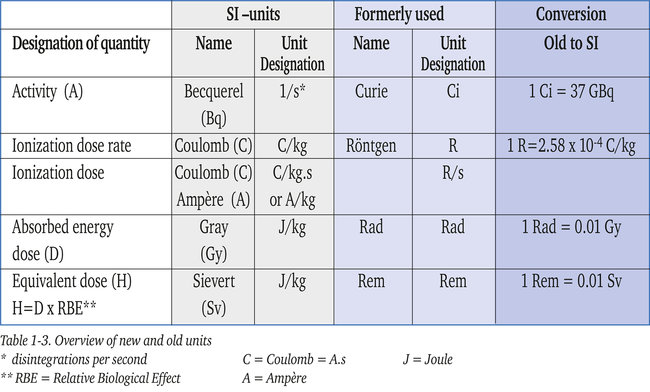
Until 1978 the “International Commission of Radiation Units and Measurements” (ICRU) used the conventional radiation units of roentgen (R), rad (rd), and curie (Ci). Since 1978 the ICRU has recommended the use of the international system units (SI) with special new units for radiation quantities; the Becquerel, Gray and Sievert. Table 1-3 shows the relationships of these new units to the older units.
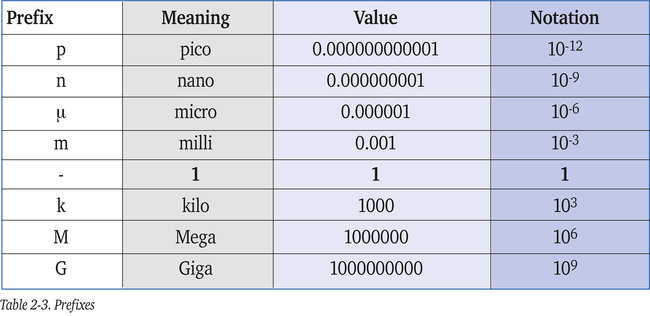
In radiography and radiation safety, units are preceded by prefixes. Table 2-3 shows the ones mostly used.
What is half-value thickness (HVT)?