Image
Image

Eyebrow
Blog
CT Operation: How Does a Digital Detector Array Work?
In this article:
- Digital Detector Arrays (DDAs) are central to modern industrial CT systems, converting X-ray shadow images into visible light using scintillator foils, which are then captured by photodiode arrays for high-fidelity imaging.
- Key advantages of DDAs include undistorted image capture, superior contrast resolution, and high dynamic range, making them ideal for precise non-destructive testing (NDT) applications.
- Temperature-stabilized DDA technology enables real-time imaging at up to 30 frames per second, enhancing inspection speed and accuracy in industrial environments.
- Advanced CT imaging with DDAs supports detailed internal structure analysis, crucial for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing.
- Waygate Technologies, a Baker Hughes business, is at the forefront of DDA innovation, driving improvements in digital radiography and computed tomography for industrial inspection.
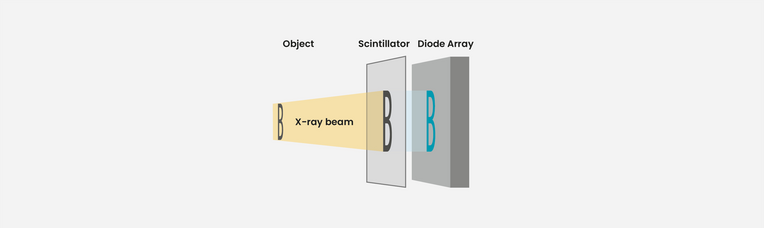
How does a digital detector array work?
The X-ray shadow image is converted by a scintillator foil to visible light which is directly detected by a photo diode array. Main advantages of this technique are the undistorted image as well as the high dynamics and the superior contrast resolution.
Latest temperature stabilized high dynamic digital detector array technology ensures brilliant live imaging with up to 30 frames per second.