Image
Image

Eyebrow
Blog
Principles of CT Operation: What is industrial cone beam computed tomography?
In this article:
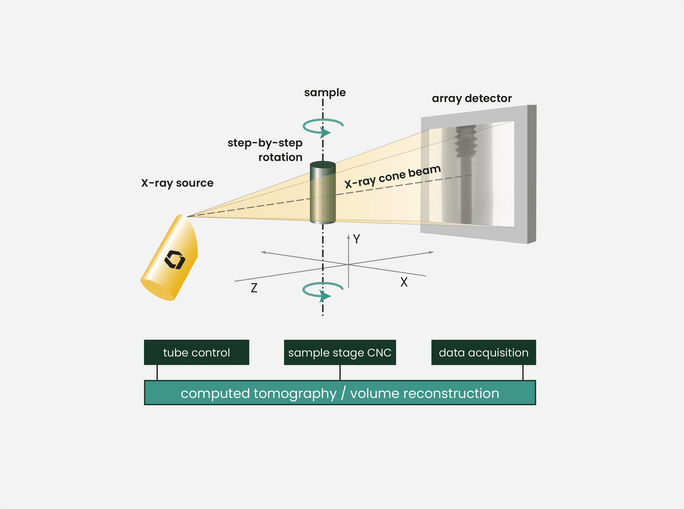
- Cone Beam CT Captures 3D Internal Structures Non-Destructively: Industrial cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) uses a cone-shaped X-ray beam and a rotating sample stage to generate high-resolution volumetric data for internal inspection
- 360° Rotation Enables Comprehensive Imaging: The object is rotated step-by-step through a full 360 degrees while 2D X-ray projections are captured, each containing density and positional data of internal features
- Volumetric Reconstruction from 2D Projections: These projections are mathematically reconstructed into a 3D model, allowing detailed analysis of internal geometries, defects, and material composition
- Ideal for Complex and High-Precision Applications: Cone beam CT is widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics for quality control, failure analysis, and reverse engineering
- Faster and More Efficient Than Fan Beam CT: While fan beam CT scans in slices, cone beam CT captures the entire volume in fewer rotations, offering faster throughput and simplified workflows for many industrial use cases
What is industrial cone beam computed tomography?
The specimen placed on a rotation table is irradiated by a cone-shaped X-ray beam so that a magnified X-ray image is produced on a detector. Generating volumetric data using industrial cone beam CT starts with the acquisition of a series of two dimensional X-ray images while progressively rotating the sample step by step through a full 360° rotation. These projections contain information on the position and density of absorbing object features within the sample. This accumulation of data is then used for the numerical reconstruction of the volumetric data.