Image
Image

Eyebrow
Blog
Principles of CT Operation: What is X-ray absorption?
In this article:
- X-ray Absorption Is the Foundation of CT Imaging: The article explains how industrial computed tomography (CT) relies on the principle of X-ray absorption to visualize internal structures of materials non-destructively.
- Material Density and Thickness Affect Absorption: Denser materials and thicker sections absorb more X-rays, resulting in darker areas on the detector image, while less dense regions appear brighter.
- Beam Hardening and Artifacts Explained: The blog discusses how lower-energy X-rays are absorbed more readily, leading to beam hardening effects and potential image artifacts that must be corrected for accurate CT scans.
- Absorption Data Enables 3D Reconstruction: By capturing multiple 2D projections at different angles, CT systems use absorption differences to reconstruct detailed 3D models of internal features.
- Critical for Quality Control and Failure Analysis: Understanding X-ray absorption is essential for optimizing CT inspection of components in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and additive manufacturing.
What is X-ray absorption?
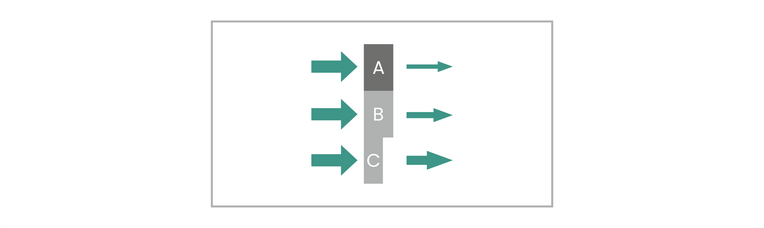
Physically, the contrast originates from different X-ray absorptions of different object areas which can be caused by varying thickness as well as by varying material:
In the below image object A is of the same thickness as object B but yields a higher absorption due to higher density or higher atomic number. Object C consists of the same material as object B but absorbs less radiation than the thicker object B.